So, we’re betting at least some of your apps and online accounts have asked, “Do you want to opt into two-factor identification?” And, if you’re like many people, all that texting and code retrieval might seem just a little too much trouble.
Is all that security really necessary? Short answer: YES. And it doesn’t have to be hard.
Why should you use two factor identification?
Cyber attacks, personal data leaks, and phishing scams are becoming more common as hackers get more sophisticated and as we conduct more of our personal and financial transactions on apps and online. Scary factoid: the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center reported that people lose $57 million in phishing and smishing schemes each year.1
Two-factor identification (2FA) provides an extra layer of protection to help safeguard your personal data and your dollars when you are accessing websites and apps.
What exactly is two-factor identification?
Also referred to as “two-step authentication,” “two-step verification” or “multi-factor authentication,” 2FA is an electronic security protocol that prevents you from accessing a website or an app until you validate your identity with two or more pieces of proof. This helps ensure that unauthorized users can’t pretend to be you.
Multi-factor identification “secures your logins from attackers exploiting weak, stolen, or leaked credentials,” says Laura Bennett, Senior Vice President, e-Consumer North America for BlinkSM by Chubb®.
How do you enable 2FA protection?
Many widely-used internet service providers (e.g. Google, Apple, Amazon) and social media platforms (e.g. TikTok, Snapchat, Facebook/Instagram), as well as financial sites, productivity, and personal apps (e.g. Paypal, Slack, Fitbit) have 2FA capability.
- A helpful website that lists sites currently offering multi-factor identification can be found here: 2FA Directory.
- Enabling 2FA is typically done through your user account and/or security tab. Instructions vary, so check with the individual sites or apps for specifics.
- There are a number of authentication apps that consolidate and streamline your 2FA efforts. In other words, the app automatically authenticates you and eliminates the code sending step. The advantages of using these are that they typically work even when you don’t have access to cell service, and they are considered more secure than text messages. Some of the most popular apps are Authy, Google Authenticator, Duo, and Microsoft Authenticator.
We do not endorse any particular vendor or brand of 2FA, but consumers should take time to research options along with the benefits of utilizing 2FA for their circumstances.
Is two-factor identification foolproof?
Currently, 2FA apps are the most secure user authentication methods. However, it is important to always practice good cyber hygiene habits:
- “Leverage alerts on all accounts (especially financial) to warn you of suspicious activity,” Bennett advises.
- Use a strong and unique username and password and never save passwords in your web browser.
- Keep your computer’s operating system up to date. This is to ensure you have the latest security features in place.
- Be wary of emails, texts, or attachments from unfamiliar or suspicious-looking senders especially those that ask for personal data.
- Avoid using open wi-fi networks, which are easily hacked.
We do not endorse any particular vendor or brand of 2FA, but consumers should take time to research options along with the benefits of utilizing 2FA for their circumstances.
Source: Chubb, the cyber insurance provider for MJ Sorority
We have seen a recent uptick in phishing scams among MJ Sorority clients. In today’s digital age, the threat of phishing is more prevalent than ever before. Did you know that over 90% of successful hacks and data breaches start with phishing scams? It’s a sobering statistic that underscores the importance of staying vigilant against this pervasive threat.
But what exactly is phishing? Simply put, it’s the process of attempting to acquire sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card or bank account details, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. Phishers often use bulk emails that try to evade spam filters, claiming to be from popular social websites, banks, auction sites, or IT administrators. It’s a form of criminally fraudulent social engineering that preys on unsuspecting individuals.
Understanding the Techniques
Phishing techniques have evolved over the years, becoming increasingly sophisticated and diverse. From traditional email and spam campaigns to more targeted approaches like spear phishing and session hijacking, cybercriminals employ a wide array of tactics to deceive their victims. They manipulate links, inject malicious content, and even resort to voice calls and SMS messages in their quest to obtain personal information.
Stay Vigilant
So, how can you protect yourself against phishing attacks? Awareness is key. Familiarize yourself with the common techniques used by cybercriminals, and adopt anti-phishing strategies to safeguard your information. Be cautious when clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources, and always verify the authenticity of requests for personal or financial information.
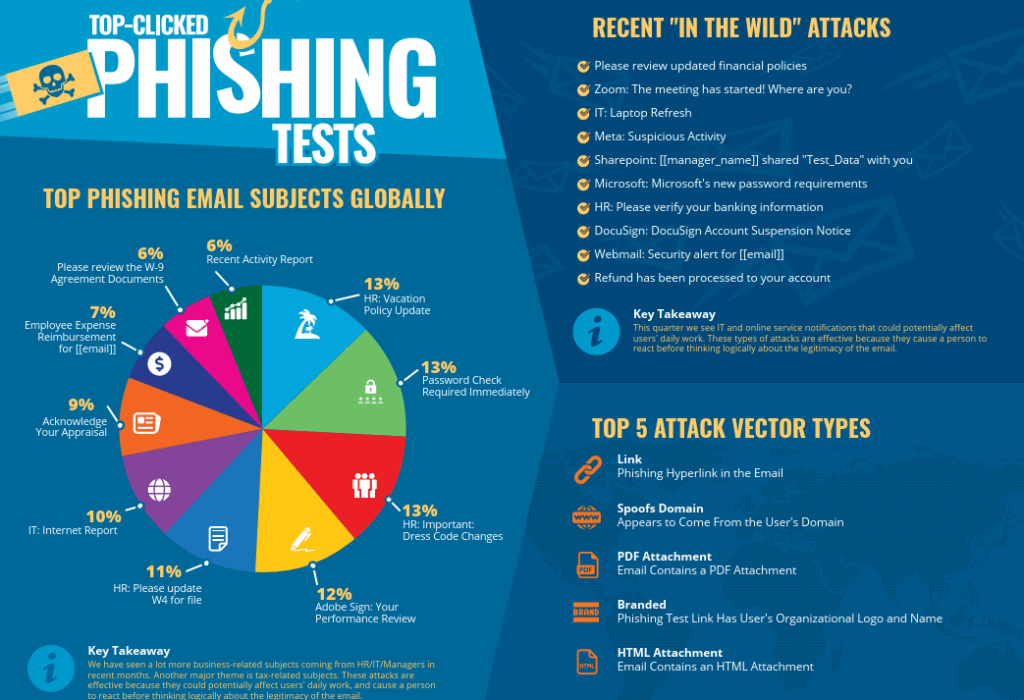
At MJ, we utilize KnowBe4, a firm that provides security awareness training to members of your organization. Each quarter, they produce an infographic with the top types of phishing attacks, as excerpted above. For the full infographic and associated data, click here. KnowBe4 also offers a free phishing security test that you can utilize to see if your employees are susceptible to phishing attacks – learn more here.





